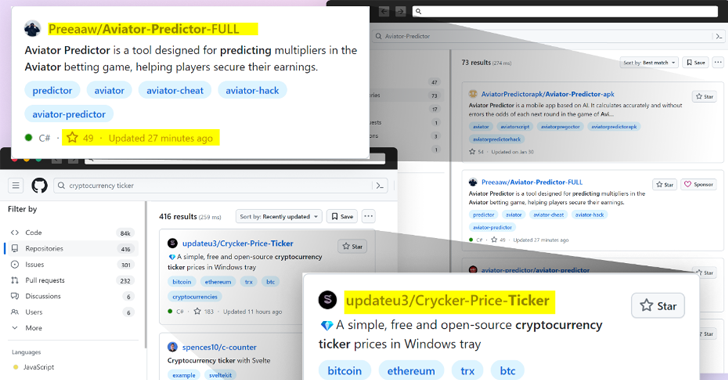
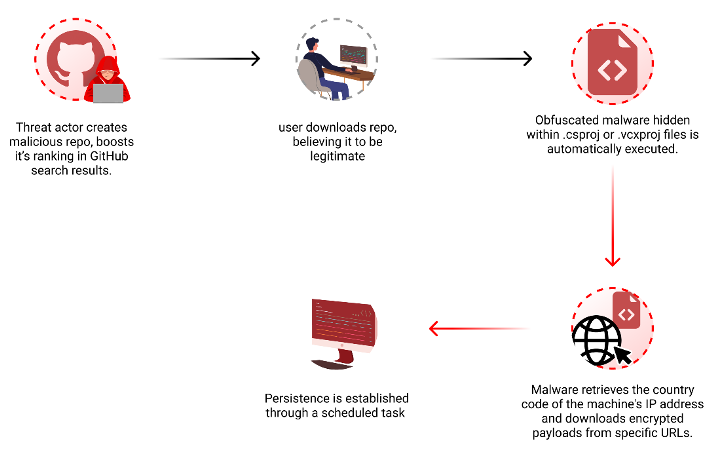
Threat actors are now taking advantage of GitHub’s search functionality to trick unsuspecting users looking for popular repositories into downloading spurious counterparts that serve malware.
The latest assault on the open-source software supply chain involves concealing malicious code within Microsoft Visual Code project files that’s designed to download next-stage payloads from a remote URL, Checkmarx said in a report shared with The Hacker News.
“Attackers create malicious repositories with popular names and topics, using techniques like automated updates and fake stars to boost search rankings and deceive users,” security researcher Yehuda Gelb said.
The idea is to manipulate the search rankings in GitHub to bring threat actor-controlled repositories to the top when users filter and sort their results based on the most recent updates and increase the popularity via bogus stars added via fake accounts.
In doing so, the attack lends a veneer of legitimacy and trust to the fraudulent repositories, effectively deceiving developers into downloading them.
“In contrast to past incidents where attackers were found to add hundreds or thousands of stars to their repos, it appears that in these cases, the attackers opted for a more modest number of stars, probably to avoid raising suspicion with an exaggerated number,” Gelb said.
It’s worth pointing out that previous research from Checkmarx late last year uncovered a black market comprising online stores and chat groups that are selling GitHub stars to artificially boost a repository’s popularity, a technique referred to as star inflation.
What’s more, a majority of these repositories are disguised as legitimate projects related to popular games, cheats, and tools, adding another layer of sophistication to make it harder to distinguish them from benign code.
Some repositories have been observed downloading an encrypted .7z file containing an executable named “feedbackAPI.exe” that has been inflated to 750 MB in a likely attempt to evade antivirus scanning and ultimately launch malware that shares similarities with Keyzetsu clipper.
The Windows malware, which came to light early last year, is often distributed through pirated software such as Evernote. It’s capable of diverting cryptocurrency transactions to attacker-owned wallets by substituting the wallet address copied in the clipboard.
The findings underscore the due diligence that developers must follow when downloading source code from open-source repositories, not to mention the dangers of solely relying on reputation as a metric to evaluate trustworthiness.
“The use of malicious GitHub repositories to distribute malware is an ongoing trend that poses a significant threat to the open-source ecosystem,” Gelb said.
“By exploiting GitHub’s search functionality and manipulating repository properties, attackers can lure unsuspecting users into downloading and executing malicious code.”
The development comes as Phylum said it discovered an uptick in the number of spam (i.e., non-malicious) packages being published to the npm registry by a user named ylmin to orchestrate a “massive automated crypto farming campaign” that abuses the Tea protocol.
“The Tea protocol is a web3 platform whose stated goal is compensating open source package maintainers, but instead of cash rewards, they are rewarded with TEA tokens, a cryptocurrency,” the company’s research team said.
“The Tea protocol is not even live yet. These users are farming points from the ‘Incentivized Testnet,’ apparently with the expectation that having more points in the Testnet will increase their odds of receiving a later airdrop.”