Cybersecurity researchers have discovered a new Linux variant of a remote access trojan (RAT) called BIFROSE (aka Bifrost) that uses a deceptive domain mimicking VMware.
“This latest version of Bifrost aims to bypass security measures and compromise targeted systems,” Palo Alto Networks Unit 42 researchers Anmol Maurya and Siddharth Sharma said.
BIFROSE is one of the long-standing threats that has been active since 2004. It has been offered for sale in underground forums for up to $10,000 in the past, according to a report from Trend Micro in December 2015.
The malware has been put to use by a state-backed hacking group from China tracked as BlackTech (aka Circuit Panda, HUAPI, Manga Taurus, Palmerworm, PLEAD, Red Djinn, and Temp.Overboard), which has a history of striking organizations in Japan, Taiwan, and the U.S.
It’s suspected that the threat actor purchased the source code or gained access to it around 2010, and repurposed the malware for use in its own campaigns via custom backdoors like KIVARS and XBOW.
Linux variants of BIFROSE (aka ELF_BIFROSE) have been observed since at least 2020 with capabilities to launch remote shells, download/upload files, and perform file operations.
“Attackers typically distribute Bifrost through email attachments or malicious websites,” the researchers said. “Once installed on a victim’s computer, Bifrost allows the attacker to gather sensitive information, like the victim’s hostname and IP address.”
What makes the latest variant noteworthy is that it reaches out to a command-and-control (C2) server with the name “download.vmfare[.]com” in an attempt to masquerade as VMware. The deceptive domain is resolved by contacting a Taiwan-based public DNS resolver with the IP address 168.95.1[.]1.
Unit 42 said it detected a spike in Bifrost activity since October 2023, identifying no less than 104 artifacts in its telemetry. It further discovered an Arm version of the malware, suggesting the threat actors are likely looking to expand their attack surface.
“With new variants that employ deceptive domain strategies like typosquatting, a recent spike in Bifrost activity highlights the dangerous nature of this malware,” the researchers said.
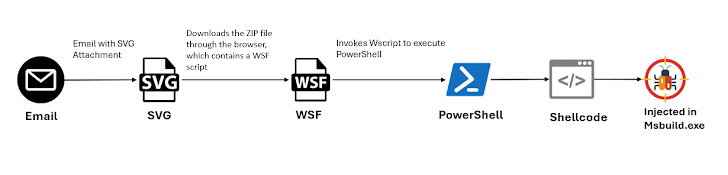
The development comes as McAfee Labs detailed a new GuLoader campaign that propagates the malware through malicious SVG file attachments in email messages. The malware has also been observed being distributed via VBS scripts as part of a multi-stage payload delivery.
“This recent surge highlights its evolving tactics for broader reach and evasion,” Trustwave SpiderLabs said in a post on X earlier this week.
The Bifrost and GuLoader attacks coincide with the release of a new version of the Warzone RAT, which recently had two of its operators arrested and its infrastructure dismantled by the U.S. government.